What is the Online Service Marketplace?
The online service marketplace is an environment in which individuals or organisations contract with independent workers for short-term, temporary engagements. It’s become an extremely hot trend in recent years, with a study by Intuit predicting that 40% of American workers would be independent contractors by 2020[1].
 [2]
[2]
How successful is the Online Service Marketplace?
The Online Service Marketplace has proven to be extremely successful. More than 1 in 3 US workers are freelancers, and as previously mentioned, this figure is expected to grow to 40% by 2020. 51% of executives in Dupress’ global survey plan to increase or significantly increase the use of contingent workers in the next 3 to 5 years, while only 16% expect a decrease[3]. Companies in all sectors—from transportation to business services—are tapping into freelance workers as a regular, manageable part of their workforces.
Business models for Online Service Marketplaces
There are altogether 3 different business models for online service marketplaces.
1. Transaction Based Model
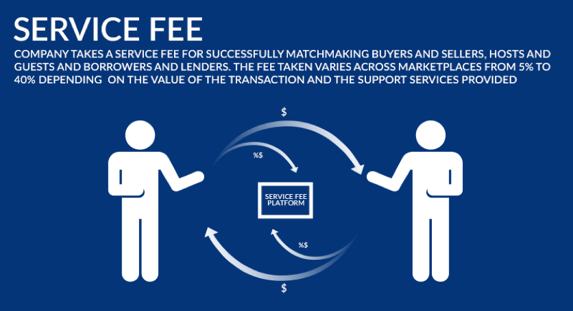 [4]
[4]
- The marketplace takes a cut of each transaction generated through the platform
Benefits:
- Customers and suppliers only pay a fee if and when they sell or buy something.
- By taking away the upfront costs of listing and the risk of not making a sale, this model encourages more suppliers to join the platform, thus increasing a marketplace’s supply.
- The more sales your platform generates, the more revenue you bring in.
- Example: TaskRabbit
2. Lead Based Model
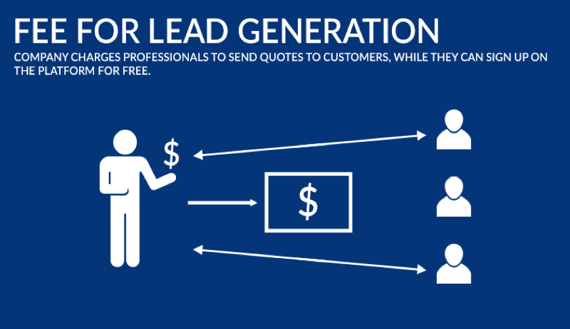
- Suppliers pay to send quotes to customers
- The platform makes introductions between customers and professionals based on the specific needs of a project. Professionals who confirm they are interested and available make bids for customers to choose from.
- The actual cost depends on the type of service the customer is looking for.
Benefits:
- As you are not asking your user base any money, it is easy to get a larger user-base fast.
- After getting them on the platform, you can easily get suppliers to participate in the marketplace with a simple up-sell.
- A lead based model gives a low-commitment way of getting on the platform to suppliers — their own web presence.
- This model of having suppliers pay to bid on a project results in more qualified options and is an easier way for customers to find the right supplier.
- Example: Thumbtack, Kaodim (potentially)
3. Subscription Based Model
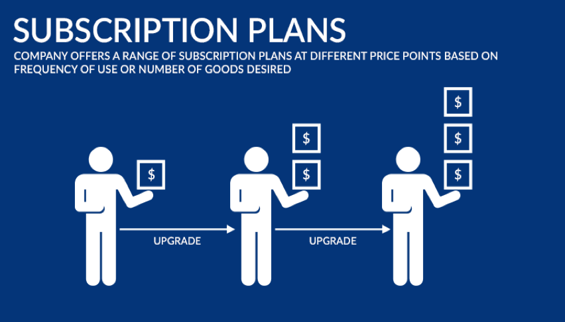
- Customers are billed on a recurring basis and receive their services at the same time every month or as per their convenience
Benefits:
- Once a customer signs up, there are high chances that they will stick around. It’s much easier to predict revenue and robust customer insight for cross-selling or marketing.
- Customers prefer to pay a low upfront expense than expensive fees for every purchase, and this model eliminates the inconvenience of buying things/services again and again. Furthermore, the monthly or other periodic payments are often offered at a discount, enhancing overall satisfaction.
- Example: Home services start-up, Alfred, lets you hire your house help starting from $22 a week, billed monthly
More details can be found in our Slideshare on the Online Gig Economy.
Commoditised and Non-commoditised service platforms
There are 2 types of service platforms in the online service marketplace:
- Commoditised service platforms
- Non-commoditised service platforms
The difference between the 2 revolves around the degree to which a product or service can be standardized. Commoditised service platforms set uniform prices for their services while non-commoditised service platforms allow individual workers to set prices for their services without regulation.
What are some challenges of running an online services marketplace?
Most services marketplaces cannot facilitate a transaction before the buyer and seller agree on the terms of the service. Actual exchange of money often follows the delivery of the service, which requires the buyer and seller to directly interact with each other. This weakens a marketplace’s ability to capture value. The party that is charged is thereby motivated to abandon the platform and conduct the transaction off-platform.
Solutions to these challenges of running an online services marketplace
To counter the challenges of running an online services marketplace, we suggest platform stickiness as a solution.
When designing a platform model, developers need to remember that workflow tools should create additional value for both sides, not just for one. For example, on Upwork, before making a hiring decision, clients have the opportunity to speak live with freelancers using built-in messaging tools. Freelancers can also evaluate prospective clients based on data such as a client’s track record for awarding posted jobs, history of job feedback, and how much a client has spent on hiring. All of these tools adds value for both users and service providers, and will make them want to continue using your platform.
It is also extremely important to build a strong on-platform reputation. Community reviews act as social proof for future clients, which in turn benefits the platform itself because suppliers would try to provide quality service to boost their ratings. For example, taskers on TaskRabbit are not only vetted before they register but are also community reviewed. Their ratings are visible to all potential task posters and they can justify their prices by the ratings they get online.
Examples of the different online service platforms
|
Company
|
Services Offered
|
Type
|
Business Model
|
|
Upwork
|
Online Outsourcing for all sorts of Freelancers
|
Non-commoditised
|
Lead Based
|
|
99 Designs
|
Graphic Design
|
Commoditised
|
Lead/Subscription Based
|
|
People Per Hour
|
Programming, Design, Administrative tasks, Accounting, PR
|
Non-commoditised
|
Transaction Based
|
|
Proz
|
Translation, Interpreting
|
Commoditised
|
Lead Based
|
|
SEO Clerks
|
SEO
|
Non-commoditised
|
Lead Based
|
|
Task Rabbit
|
House Cleaning, Moving, Delivery and Handyman Work
|
Non-commoditised
|
Transaction Based
|
|
Writer Bay
|
Academic Writing
|
Commoditised
|
Lead Based
|
|
DogsVacay
|
Pet Sitting
|
Non-commoditised
|
Transaction Based
|
|
OpenTable
|
Restaurant Reservations
|
Non-commoditised
|
Transaction/ Subscription Based
|
|
Zeel
|
In-Home Massage
|
Commoditised
|
Transaction/ Subscription Based
|
|
Thumbtack
|
Online outsourcing for freelancers
|
Non-commoditised
|
Lead Based
|
|
AirFrov
|
Online marketplace for buyers to get travelers to bring back products from overseas
|
Non-commoditised
|
Transaction Based
|
|
Foodpanda
|
Food Delivery
|
Non-commoditised
|
Transaction Based
|
Case Study: Kaodim
In order to visualize how an online marketplace works, let’s do a case study on Kaodim. Kaodim is a Malaysia-based online service marketplace which allows people to find, compare and hire service professionals. It adopts a non-commoditised, lead-based business model.
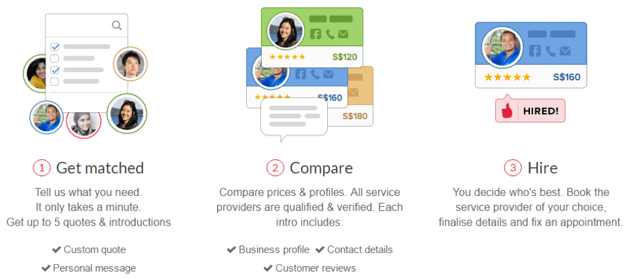
Who can be a Kaodim service provider?
- Registered businesses
- Freelancers
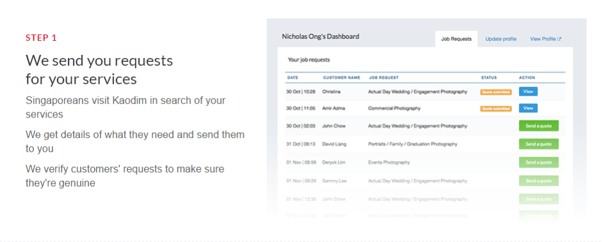
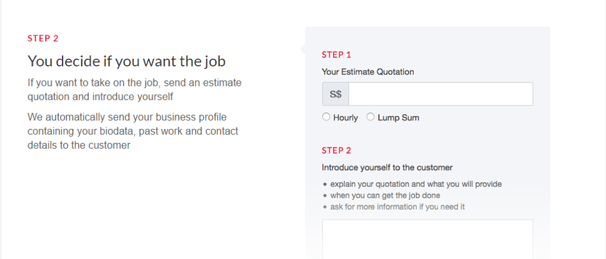
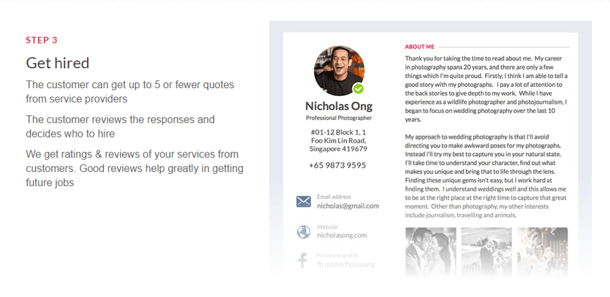
What kind of services can you find on Kaodim?
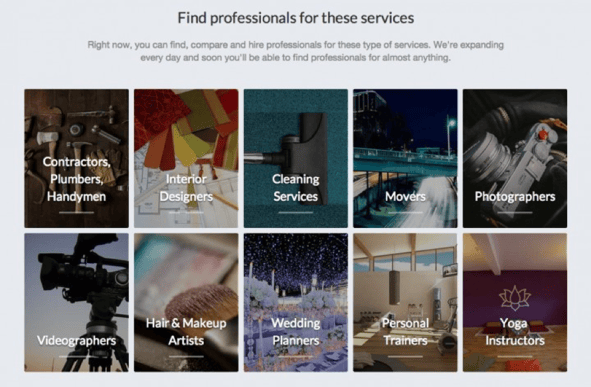
What are the benefits of Kaodim?
Kaodim saves people the time and effort of hunting down the right service provider and is free-of-charge for all users. On top of that, customers are also assured of the quality of service providers based on community reviews.
Traditionally, service providers pay a static monthly fee – which can be fairly expensive – to have their services listed on other directories or online advertisements, which does not necessarily translate into customers. Kaodim empowers providers with the knowledge of who needs their services and when they need it, allowing them to get hired in an efficient manner.
[1] http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/gig-economy
[2] http://www.fatbit.com/fab/service-professional-marketplace-work-feature-analysis-deciphers/
[3] http://dupress.com/articles/gig-economy-freelance-workforce/
[4] http://nextjuggernaut.com/blog/how-to-succeed-with-a-services-marketplace-choose-the-model-that-fits-you-right/